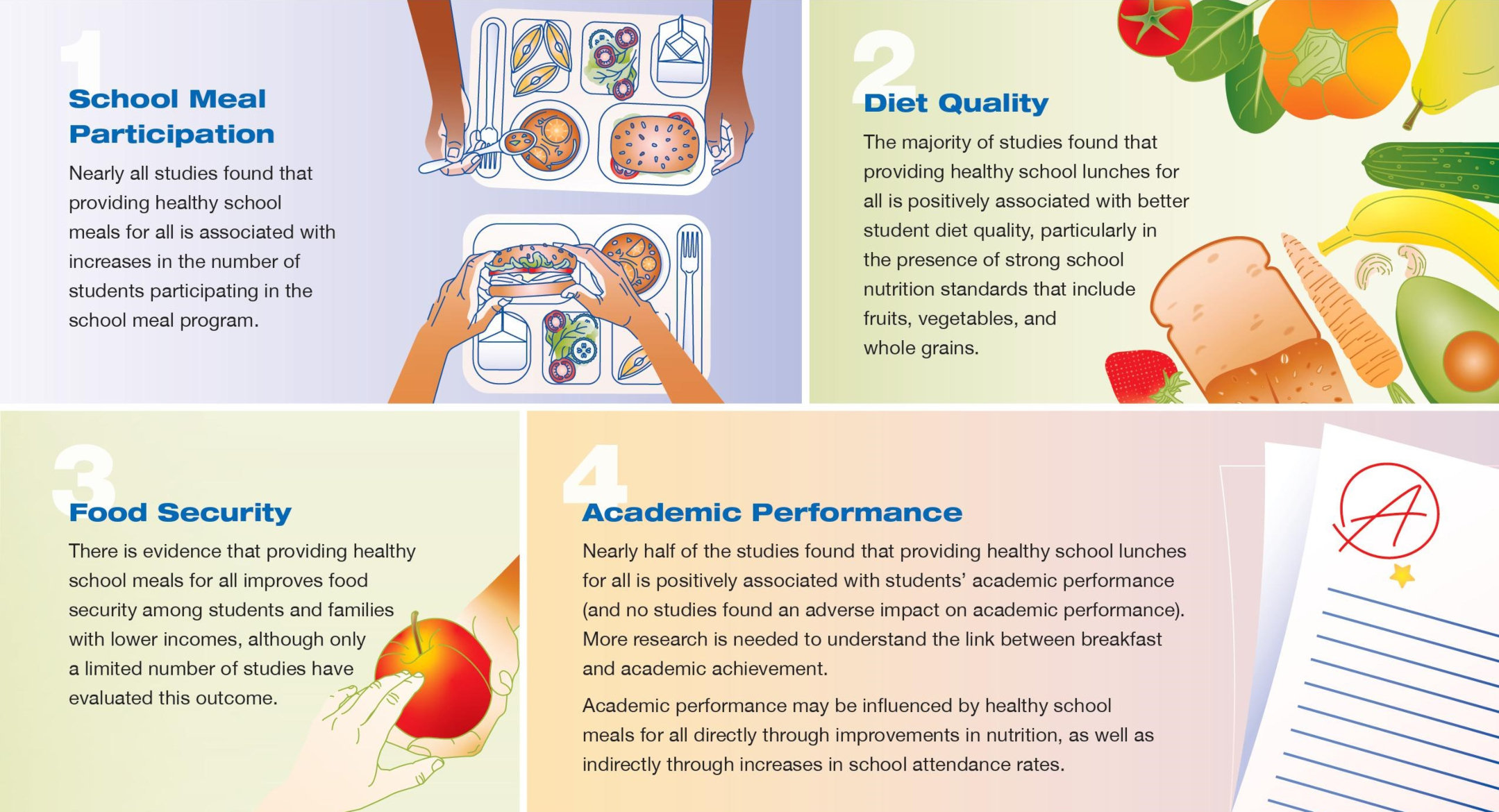
In recent years, the relationship between nutrition and academic performance has garnered increasing attention from educators, parents, and policymakers. Research indicates that nutrition education can significantly influence students’ academic outcomes, leading to better grades, improved concentration, and enhanced overall well-being. This article explores the multifaceted impact of nutrition education on student academic performance, highlighting its importance in the learning environment.

Understanding Nutrition Education
Nutrition education encompasses a range of activities designed to teach individuals about the importance of healthy eating habits and nutritional choices. In schools, this education may take the form of classroom instruction, hands-on cooking classes, or school-based health initiatives. The goal is to empower students with knowledge about nutrition, enabling them to make informed choices that support their health and academic success.
The Link Between Nutrition and Academic Performance
Numerous studies have established a clear connection between nutrition and cognitive function. The brain requires a steady supply of nutrients to operate efficiently. Essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids, play crucial roles in brain development and function. For instance, deficiencies in these nutrients can lead to decreased cognitive performance, memory issues, and difficulties with concentration.
Improved Concentration and Behavior
Students who receive proper nutrition are often better equipped to focus in the classroom. A well-balanced diet supports neurotransmitter function, which is vital for attention and information processing. Research has shown that children who consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins exhibit improved concentration and reduced behavioral issues compared to their peers with poor dietary habits. This improvement in focus allows students to engage more fully in lessons, participate in discussions, and complete assignments efficiently.
Enhanced Memory and Retention
Nutrition education helps students understand the importance of eating foods that support brain health. For instance, foods high in antioxidants, such as berries and leafy greens, can enhance memory and cognitive function. Furthermore, the consumption of omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and flaxseeds is linked to improved memory retention and learning capabilities. By instilling these principles through nutrition education, students can make better food choices that positively affect their academic performance.
The Role of Breakfast
One critical aspect of nutrition education is the emphasis on the importance of breakfast. Studies consistently show that students who eat a healthy breakfast tend to perform better academically than those who skip it. Breakfast provides essential nutrients and energy that help maintain alertness and concentration throughout the morning. Schools that implement breakfast programs have observed increased attendance rates and improved test scores, underscoring the need for accessible breakfast options as part of nutrition education initiatives.
Addressing Food Insecurity
Food insecurity remains a significant barrier to academic success for many students. Nutrition education programs that address this issue can play a vital role in improving student outcomes. By providing information on budgeting for healthy meals, cooking skills, and access to community resources, these programs can help families make healthier choices despite financial constraints. Schools that integrate nutrition education with food assistance programs create a supportive environment that fosters both academic achievement and overall well-being.
Promoting Healthy Habits Beyond the Classroom
The impact of nutrition education extends beyond academic performance; it also fosters lifelong healthy habits. When students learn about nutrition in school, they are more likely to carry these lessons into adulthood, making healthier food choices and maintaining a balanced diet. This long-term approach not only benefits individual students but also contributes to a healthier society overall. As these students grow into adults, they are better equipped to make informed decisions about their health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases related to poor nutrition.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of nutrition education are clear, several challenges must be addressed to maximize its impact. First, there is the need for trained educators who can effectively deliver nutrition education. Many teachers lack the knowledge or resources to provide comprehensive nutrition education, which can limit its effectiveness. Additionally, curriculum standards often prioritize core subjects like math and reading, leaving little room for health education.
Moreover, cultural differences and varying socioeconomic factors can affect students’ perceptions of nutrition. Tailoring education to meet the diverse needs of students is essential for fostering an inclusive learning environment.
Conclusion
The impact of nutrition education on student academic performance is profound and multifaceted. By promoting healthier eating habits, improving concentration and memory, and addressing food insecurity, nutrition education empowers students to reach their full potential academically. As schools and communities recognize the importance of this connection, they can implement effective nutrition education programs that not only enhance academic success but also contribute to the overall health of future generations. Investing in nutrition education is not just a matter of academic achievement; it is an investment in the well-being and future of our society.



